In the background I have been mulling over whether to attempt to draft a patent application concerning quantum telepathy as it might be applied to the current groovy quantum area. This morning between a sleep and waking a question appeared to mind, “Quantum Telepathy or Quantum Telekinesis?”
I’ll make an initial comment.
It is safe for me to publicly publish my speculations on-line because in no way can they detrimentally harm any career of mine at some august institution into which I might have been sectioned under the mental health act. I am free to make a fool or an arse of myself because it cannot negatively impact on tenure or promotion.
There has been a lot of interest in things called parapsychology among the public if not academia. Taboos remain. The notions of telepathy and telekinesis have not yet been proven extant, though they are found throughout culture and in some cases religion. We have Professor Charles Xavier and the X-men, we have spoon benders. In Buddhism we have Abhijñā or higher powers.
—————
Abhijñā
In the Pali Canon, the higher knowledges are often enumerated in a group of six or of three types of knowledge.
The six types of higher knowledges (chalabhiññā) are:
- “Higher powers” (iddhi-vidhā), such as walking on water and through walls;
- “Divine ear” (dibba-sota), that is, clairaudience;
- “Mind-penetrating knowledge” (ceto-pariya-ñāṇa), that is, telepathy;
- “Remember one’s former abodes” (pubbe-nivāsanussati), causal memory, that is, recalling one’s own past lives;
- “Divine eye” (dibba-cakkhu), that is, knowing others’ karmic destinations; and,
- “Extinction of mental intoxicants” (āsavakkhaya), upon which arahantship follows.
From Wikipedia
——————
Your common or garden scientist is unlikely to have much credulity for these, though the script writer might. There have been experiments to test extra sensory perception using inter alia Zener cards.
—-

—–
I don’t know about you, but these images a very boring, I could have used the F word in participle here. Who in their right mind would be excited to transmit or receive these? Not me, YAWN.
If you were to construct an experiment on telekinesis without Magneto you might want to start with the tiniest measurable change, something with a vanishing mass something like 1×10−18 eV/c2. In other words photons. If the mind can move anything or change anything then photons are a good starter for ten. They move quick but don’t weigh much.
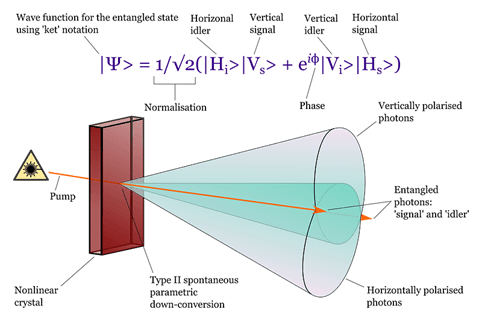
In the field of quantum technology one branch pertains to spontaneous parametric down conversion. In this a single photon is “destroyed” “annihilated” and two daughter photons are “created”. Momentum of all types ought to be conserved. Under low light level conditions these daughter photons can be created in a quantum superposition state. Where their polarisation is a mix of horizontal and vertical polarisation, that is until said state in measured. If you measure one photon to have vertical polarisation then the other must have horizontal polarisation. The quantum superposition state collapses. The two photons somehow have information about the state of each other. This transfer of information is a faster than speed of light thing. One photon says on measurement, “hey, I am vertical” and telepathically the other photon knows “I am horizontal.” The photons have a mind of their own and unless they are really clever, they do not know how we label them or describe them. They do not care what we think or how we describe.
The photons could, to stretch things, be said to be in telepathic rapport with each other.
—-
—-
At the single photon level the notion of polarisation is a bit tricky. Polarisation is a wave-like, multiphoton, phenomenon. It describes how a bunch of photons pass through a selective physical device. There is a bit of magic between the descriptions of single photons and the more bulk properties, perhaps a grey area of science in the statistics of low particle count number. A single photon may fail to pass through a polarisation gate which means that its twin photon is allowed to go through, to get past the bouncers and into the night club. If the first photon is not on the guest list, its twin must be.
The physics when carried out over many events predicts well the number of horizontal and vertical photons. The detection of a horizontally polarised photon accurately predicts the arrival in time, and hence path length, of its erstwhile conjoined twin. The first observation operation separates the conjoined twins. One can accurately time bin polarisation heralded photons.
We now have a candidate scenario for a parapsychology experiment which has a miniscule change in terms of mass {momentum} and a binary change in terms of information.
If one was to try to influence the weighting of the quantum superposition state, the entangled state, in the equation above one could perturb the normal statistically verifiable distribution. In the equation above the horizontal and vertical are given equal weighting, 50:50 not ‘phone a friend.
By telepathy one might read and perhaps alter the information, by telekinesis one might rotate the polarisation sate weighting in the entangled pair. Conferring a more horizontal bias to one of the conjoined pair. It would be semantic if it is information or property which is altered.
To meditate in a dark room with lasers is not to everyone’s taste. It was once to mine, the so-called Zen of laser alignment. It is a good, isolated environment for experimentation.
I think I might have the bones of an experiment which offers more likelihood of success than trying to mind-to-mind boring cards.
—
—
